Multiple Choice Points Awarded. ΔHv is the difference between the enthalpy of the saturated vapor and that of the saturated liquid at the same temperature.
It is in effect being stored in the water.

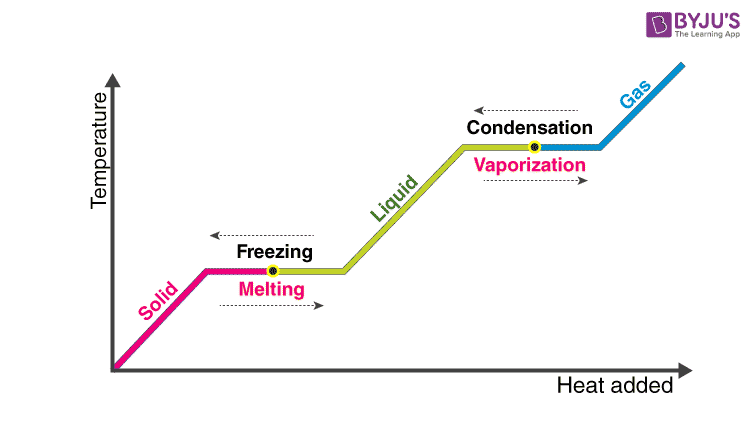
. Technical term is phase change. From solid to liquid. That associated with vaporizing a liquid or a solid or condensing a vapour is called the heat of vaporization.
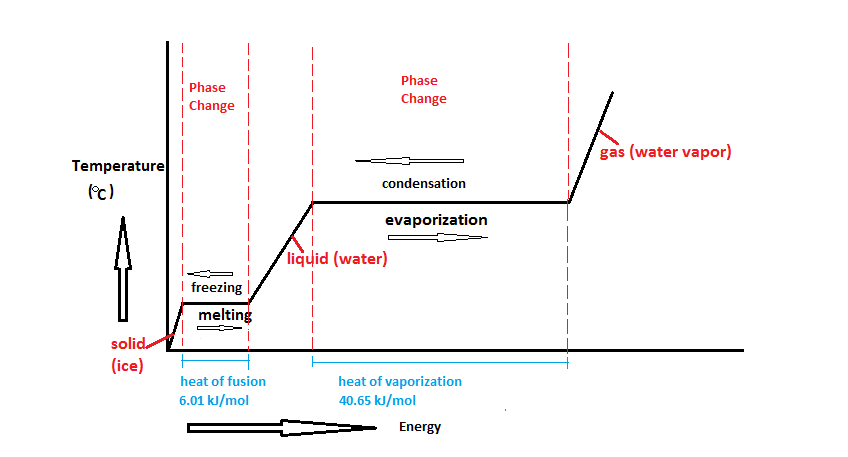
Heat energy absorbed during a. The latent heat associated with melting a solid or freezing a liquid is called the heat of fusion. The heat consumed or emitted when matter melts changing state from solid to fluid-structure at a constant temperature is known as latent heat of fusion.
Two common forms of latent heat are latent heat of fusion melting and latent heat of vaporization boiling. Specific latent heat is the amount of energy required to change the state of 1 kilogram kg of a material without changing its temperature. The heat or energy consumed or emitted during a phase change of a material is known as latent heat.
The heat of condensation the heat of vaporization and so on are some of the names given to it depending on the different phases. These names describe the direction of energy flow when changing from one phase to the next. The enthalpy of vaporization data is used in process calculations such as the design of relief systems involving volatile compounds.
Gas to Liquid Evaporation. Best Custom Writings. Test QuestionsWhich of the following best describes the role of latent heat it comes from condensation in the cloud formation processWhich of the following p.
As defined by Websters Dictionary latent means present and capable of emerging or developing but not now visible obvious active or symptomatic The transition from ice to vapor bottom and from vapor to ice top. Learning Objectives Describe the latent heat as a form of energy Key Takeaways Key Points Energy is required to change the phase of a substance such as the energy to break the bonds between molecules in a block of ice so it may melt. Question 13 Which of the following best describes latent heat.
Rain or Snow Runoff. Test Questions Which of the following best describes the role of latent heat it comes from condensation in the cloud formation processWhich of the following phase changes causes H2O molecules to lose heat energyAir cooling in result of pressure changes is known asWhich of the following best describes the order that cloud forming processes occurWhich. The heat transfer from molecule to molecule both of which must be touching O B.
The main difference between latent heat and sensible heat is that latent heat is defined for a system that undergoes a phase. The quantity of heat which is absorbed or released by a substance during a change of state fusion or vaporization at constant temperature. Latent heat energy absorbed or released by a substance during a change in its physical state phase that occurs without changing its temperature.
This hidden heat is referred to as latent heat. Water settles into soil correct Question 3. Latent heat describes the changes in the internal energy of a system whereas sensible energy describes the energy exchange between a system and its surrounding.
As there are two boundaries solidliquid and. Latent heat and sensible heat are two forms of energy. It could either be from a gas to a liquid or liquid to solid and vice versa.
Get Perfect Grades Consistently by Using Our Service 1 718 717 2861 44 161 818 7126 email protected Skip to content. The latent heat is the energy associated with a phase change of a substance. For example the additional heat required for turning water into water vapor or on the contrary the heat released when vice versa happens.
See all related content. Sensible heat affects dry-bulb temperature whereas latent heat affects moisture content. The enthalpy of vaporization ΔH v is also termed the latent heat of vaporization.
A phase change is the change of a substances physical state. The latent heat of vaporization LHOV for the fuel is the amount of required energy which changes the state of fuel from liquid to gas without a change in temperature. A net transfer of heat upward away from the surface O D.
Heat of fusion is the latent heat associated with melting a solid or freezing a liquid. Potential energy latent heat. Latent heat is defined as the heat or energy that is absorbed or released during a phase change of a substance.
Heat energy absorbed or released during a change of state of water Correct Answers. Latent heat is described as the amount of energy that is absorbed or released for a substance to change its state. Latent heat is energy released or absorbed by a body or a thermodynamic system during a constant-temperature process.
-when liquids turn into gas. Latent heat Characteristic amount of energy absorbed or released by a substance during a change in physical state that occurs without a change in temperature. The heat energy required to transform a solid into a fluid at atmospheric pressure is the latent heat of fusion while the temperature remains constant during the operation.
Water vapor water because of condensation. Latent Heat of Fusion. User Answer Correct Latent heat is best described as.
This parameter is expressed in unit kJkg which is the value of heat energy to turn one kilogram of fuel from the liquid state to a gaseous vapor. Latent heat is related to a heat property called enthalpy. Heat released or absorbed when a substance changes state without a change in temperature.
-happens at boiling point. The annual purchased energy saved by a passive heating system compared to a building heated by a conventional heating system The primary difference between sensible and latent heat is. Latent heat is the energy required to change the state of a substance from solid to liquid and vice-versa as well as from liquid to gas and vice-versa and from the solid state to the gaseous state and vice-versa without changing the temperature of the substance.
Heat that changes the state not the temperature. Latent heat is the heat used to convert a solid to a liquid or vapour phase or a liquid to a vapour phase. The latent heat definition describes the amount of energy that is released or absorbed during a phase change at a constant temperature.
Liquid to Gas Precipitation. The horizontal transport of energy in the atmosphere. The heat absorbed or released per unit mass when water changes phase O C.
What Is Latent Heat Of Fusion And Vaporization How Do They Differ From Each Other Quora
Latent Heat Definition Types Formula Fusion And Vaporization

0 Comments